Modern websites are no longer just “websites.” They are ecosystems that power mobile apps, SaaS dashboards, eCommerce stores, smart devices, and future platforms that don’t even exist yet. This shift has pushed traditional web architecture to its limits and led to the rise of headless web development.
If you’ve ever wondered what does headless mean in web development, you’re really asking why developers are separating design from data, why APIs are central to modern websites, and how brands achieve speed, scalability, and omnichannel delivery at once. This guide explains the concept in depth, without buzzwords, and gives you the most complete, practical answer available online.
Short Answer — What Does Headless Mean in Web Development?
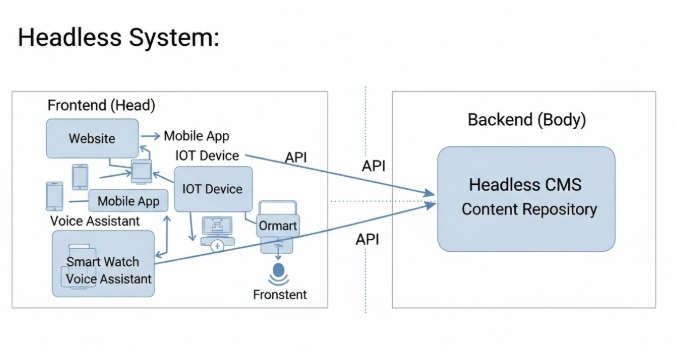
Headless in web development means the frontend (the “head” that users see) is completely separated from the backend (where content, data, and logic live), with communication handled through APIs instead of tightly coupled templates.
This matters because it allows developers to build faster, more flexible websites and deliver the same content to multiple platforms without rebuilding the backend each time.
Core Explanation of Headless Architecture in Web Development
To understand headless, it helps to compare it with how websites were traditionally built.
Traditional (Monolithic) Web Architecture Explained
In a traditional setup:
- The backend manages content, databases, authentication, and business logic
- The frontend is rendered by the same system using themes or templates
- Content, layout, and logic are tightly connected
Examples include classic WordPress themes, PHP-based CMS platforms, and older eCommerce systems. While simple, this approach creates limitations:
- Frontend changes can break backend logic
- Scaling performance is harder
- Supporting mobile apps or new platforms requires workarounds
What “Head” and “Body” Mean in Technical Terms
- Head: The presentation layer (HTML, CSS, UI, layouts, rendering)
- Body: The backend (content storage, APIs, authentication, business rules)
In headless web development, the “head” is removed from the backend entirely.
How APIs Replace Tight Frontend/Backend Coupling
Instead of rendering pages, the backend:
- Stores structured content
- Exposes data via APIs (REST or GraphQL)
- Sends raw data to any frontend that requests it
The frontend then decides how, where, and when to display that content.
Why Headless Emerged
Headless architecture became popular because it solves modern challenges:
- Scalability: Backend and frontend scale independently
- Omnichannel delivery: One backend powers web, mobile, IoT, and more
- Performance: Frontends can be optimized with modern frameworks and CDNs
- Developer flexibility: Teams choose best-in-class tools
What Does Headless Mean in Web Development at a Technical Level?
At a technical level, headless web development is about separation of concerns.
Separation of Concerns
Each layer has a clear responsibility:
- Backend focuses on data and logic
- Frontend focuses on UI and user experience
This reduces complexity and makes systems easier to maintain.
Role of APIs (REST and GraphQL)
APIs act as the bridge:
- REST APIs deliver data through endpoints
- GraphQL allows precise data queries
- Both enable multiple frontends to consume the same backend
Frontend Frameworks Commonly Used
Headless frontends are often built with:
- React
- Next.js
- Vue
- Nuxt
- Svelte
These frameworks enable fast rendering, dynamic interfaces, and SEO-friendly output when used correctly.
Backend Responsibilities in a Headless Setup
The backend handles:
- Content management
- Authentication and permissions
- Business rules
- Data validation
- API security
Sub-Questions Users Also Ask (People Also Ask)
Is headless the same as decoupled?
Not exactly. All headless systems are decoupled, but not all decoupled systems are fully headless. Headless removes the presentation layer entirely.
Is headless only for CMS platforms?
No. Headless applies to CMSs, eCommerce platforms, SaaS backends, and custom applications.
Do you need JavaScript for headless?
In most cases, yes. Modern headless frontends rely heavily on JavaScript frameworks.
Is headless better for SEO?
It can be, but only when implemented correctly using server-side rendering or static generation.
Is headless more expensive?
Initial development can cost more, but long-term scalability and reuse often reduce total cost of ownership.
How Headless Web Development Works
Choose a Headless Backend
Select a backend such as:
- A headless CMS (e.g., Contentful, Strapi)
- A custom API backend
Structure Content and Data Models
Define structured content:
- Articles
- Products
- Users
- Metadata
This structure determines how content is reused across platforms.
Expose Data via APIs
Create API endpoints that deliver content securely and efficiently.
Build the Frontend (“Head”)
Use a modern framework to:
- Render content
- Handle routing
- Optimize performance
- Control UI/UX completely
Step 5: Connect Frontend to Backend
Fetch data from APIs and map it to UI components.
Step 6: Deploy and Scale Independently
Frontend and backend can be deployed, updated, and scaled separately without downtime.
Headless vs Traditional Web Development
| Feature | Headless Web Development | Traditional Web Development |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Fully decoupled | Tightly coupled |
| Frontend Flexibility | Extremely high | Limited by templates |
| Performance | Optimized with modern frameworks | Depends on backend rendering |
| SEO | Excellent when implemented correctly | Good by default |
| Scalability | Independent scaling | Monolithic scaling |
| Omnichannel Support | Native | Limited or complex |
| Development Complexity | Higher upfront | Lower upfront |
| Long-Term Flexibility | Very high | Limited |
FAQs About Headless Web Development
What does “headless” actually refer to?
It refers to removing the frontend presentation layer from the backend system.
Is headless web development good for beginners?
It’s better suited for intermediate to advanced developers due to added complexity.
Can headless be used for small websites?
Yes, but it may be overkill unless future growth or omnichannel delivery is planned.
Does headless improve website speed?
Often yes, especially when combined with static generation and CDNs.
How does headless affect content editors?
Editors work in a structured content interface instead of visual page builders.
What are common headless CMS examples?
Contentful, Sanity, Strapi, Prismic, and Ghost (headless mode).
Is headless future-proof?
Yes. Its flexibility makes it well-suited for emerging platforms and technologies.
When should you not use headless?
Avoid it for simple sites where speed to launch and low cost matter more than flexibility.
Conclusion — When and Why Headless Web Development Makes Sense
So, what does headless mean in web development in practical terms? It means freedom freedom to design without backend limitations, to scale without refactoring, and to deliver content anywhere users exist.
Headless web development makes sense when:
- You need performance and scalability
- You plan to support multiple platforms
- You want long-term architectural flexibility
- You have the technical resources to implement it properly
For simple websites, traditional approaches still work well, you should contact Incline Solution for proper website creation. But for modern, growth-focused digital products, headless architecture is increasingly becoming the standard not the exception.


Leave a comment